What are the Best Uses for a Wood Router?
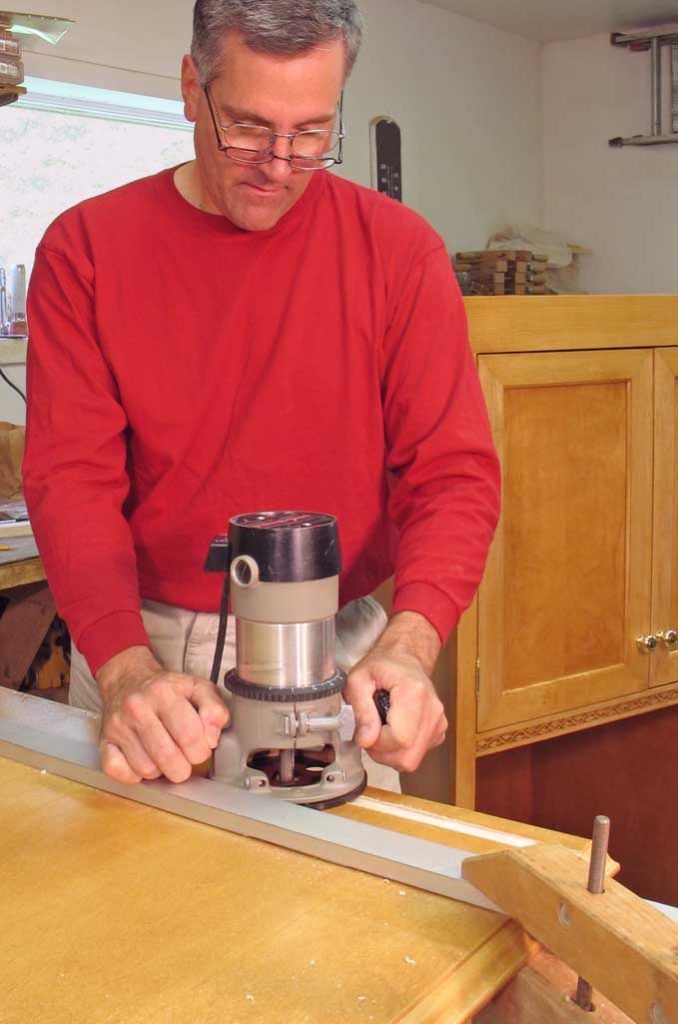

A wood router is one of the most versatile and useful power tools for any woodworking project. Routers are handheld or stationary tools that use high-speed rotating bits to cut, shape, and decorate wood. With the right router bits and techniques, routers can add an endless array of decorative details as well as joinery and functional elements to your woodworking projects.
In this article, we will discuss what a wood router is, the types available, essential features, and most importantly – the best uses for a wood router in woodworking projects. Understanding the capabilities and limits of these indispensable tools is key to getting the most out of your wood router.
What is a Wood Router?
A wood router is a handheld or stationary power woodworker tool that spins a router bit at a very high speed to cut and shape wood. The speed generally ranges from 8,000 to 30,000 rpm depending on the size and power output. Routers have an electric motor that spins the router bit, while the baseplate provides stability and precision in guiding the router tool. Routers shape, trim, cut grooves and joints, decorate edges, carve patterns, and more in woodworking.

Different Types of Routers
There are two main types of routers – plunge routers and fixed/standard routers.
Fixed Base Router
The fixed-base router is the most straightforward type, excelling in straight-line routing and edge shaping.
Features
- Stability: Offers a stable base for precise cuts.
- Ease of Use: Ideal for beginners.
- Applications: Great for edging and chamfering.
Plunge Router
The plunge router is designed to allow the bit to be lowered into the material, making it the go-to choice for interior cuts.
Features
- Versatility: Suitable for complex tasks like engraving and inlaying wood.
- Depth Control: Allows for adjustable depth settings.
- Applications: Perfect for dovetails and box joints.
Comparison Between Fixed-Base and Plunge Routers
| Feature | Fixed-Base Router | Plunge Router |
|---|---|---|
| Versatility | Less versatile | More versatile |
| Ease of Use | Easier to use | More difficult to use |
| Depth of Cut | Limited depth of cut | Deeper depth of cut |
| Safety | Safer | Less safe |
Combo Router
The combo router is like having the best of both worlds. It features both fixed and plunge bases, which you can switch between depending on the task at hand.
Features
- Flexibility: Switch between bases for different tasks.
- Cost-Effective: More economical than buying two separate routers.
- Applications: Suitable for both edge work and interior cuts.
CNC Router
Overview
Computer Numerical Control (CNC) routers are the future of woodworking. These are automated machines controlled by software.
Features
- Precision: Extremely accurate for complex designs.
- Speed: Faster than manual routing.
- Applications: Ideal for intricate patterns and mass production.
Palm Router
Overview
Palm routers are the compact, lightweight cousins in the router family, designed for small-scale tasks.
Features
- Portability: Easy to handle and maneuver.
- Convenience: Ideal for quick, small jobs.
- Applications: Best for trimming and shaping wood.
Router Table

Though not a type of router in the traditional sense, a router table allows you to mount any router upside down for stationary work.
Features
- Stability: Provides a stable work surface.
- Versatility: Compatible with various router types.
- Applications: Useful for tasks requiring precision and stability.
Essential Components of a Wood Router
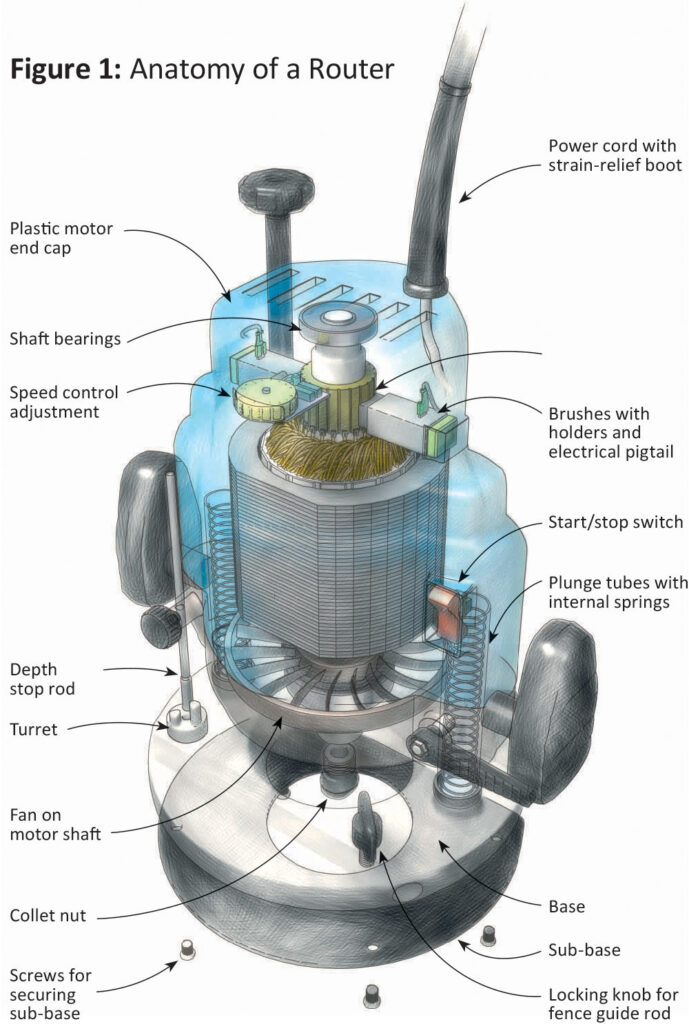
A wood router mainly consists of a motor, base, bit changing mechanism (collet), edge guide, depth adjustment system, speed control, and switch. Key features include:
- Motor – Determines power and max bit sizes. Common horsepower ratings are 1 to 3 HP.
- Base – Controls stability and swivel for handheld use. Plunge routers have bases that move up and down.
- Collet – Holds router bits securely. May be 1/4-inch or 1/2-inch.
- Depth adjustment – Controls cutting depth and exposes the bit progressively.
- Edge guide – Used to guide the router in straight lines or circles.
- Speed control – Allows adjustment of router bit RPM as per needs.
- Switch – On/off switch with lock for safety. Some have variable speed triggers.
Router Bit Types and Their Uses
| Router Bit Type | Best Use Case | Skill Level Required |
|---|---|---|
| Straight Router Bit | Cutting straight grooves, dadoes, and rabbets | Beginner |
| Round-over Router Bit | Creating rounded edges | Beginner |
| Cove Router Bit | Cutting concave curves | Intermediate |
| Chamfer Router Bit | Creating angled edges | Beginner |
| Ogee Router Bit | Cutting decorative curves | Intermediate |
| Roman Ogee Router Bit | Cutting S-shaped curves | Intermediate |
| Spiral Router Bit | Cutting precise grooves and profiles | Expert |
| Inlay Router Bit | Cutting grooves for inlays | Expert |
| Finger Joint Router Bit | Cutting finger joints | Expert |
Best Uses for a Woodworking Router Guide
Now that we have understood what a wood router is and what it’s made of, let’s get into the many applications and uses of this essential woodworking power tool:
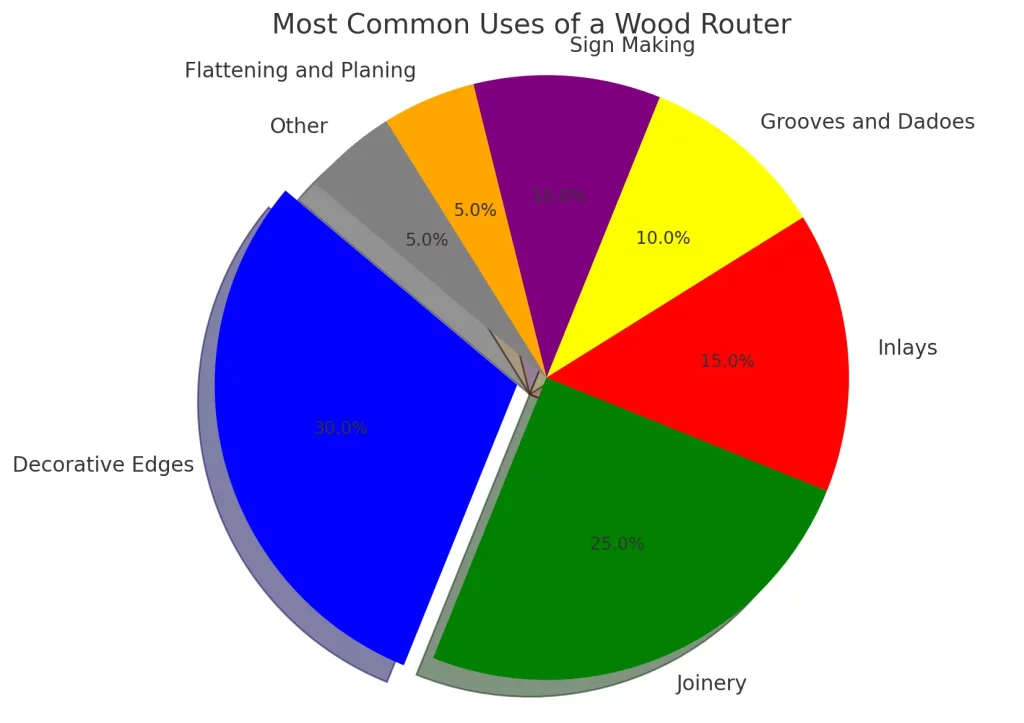
Routered Edges and Profiles
One of the most common uses of a router is to decorate and shape the edges of boards and tables. With a huge variety of router bit profiles, you can create any edge shape imaginable.
Common edge treatments include:
- Roundovers – Rounded, smooth edges
- Bevels – Angled edges and recesses
- Chamfers – Beveled edges
- Ogees – S-shaped edges
- Coves – Concave recessed edges
- Fillet – Curved convex edges
Routers shape edges by guiding the spinning router bit along the edge at the right depth. The options are virtually endless. Make straight, wavy, or irregular organic edges.
With the right router bits like spirals, you can create fluted columns, grooved textures, and more on your wood projects.
Joinery and Dovetailing
Routers allow you to make strong and beautiful joints like dovetails easily with precision – something that would be extremely complex using handsaws.
Dovetails are interlocking joints used in drawers, boxes, carcass, and fine furniture. The precision interlocking “tails” and “pins” create very strong joints. Using a dovetail jig on a router makes perfect fitting joints easy to achieve with cleaner cuts than handsaws.
Other joints like rabbets and dadoes, grooves, lap joints, mortise-tenons, box joints, finger joints, and many more are easily achieved on a wood router using straight, spiral, dovetail, and slot cutting bits. This allows crafting very strong joinery for all types of woodworking projects.
Routing Recesses and Grooves
Recesses and grooves allow inserting panels, glass, flooring, and joinery accurately within constructions like cabinets, tables, frames, and boxes. This is easily achieved by equipping the router with a straight bit and setting the right depth for a stopped groove or running groove.
By running the router baseplate along a straightedge, precise grooves can be cut for inserting panels, tongues and grooves, inlays, and more. Stopped grooves allow the inserting of floating panels to neatly. Adjustable edge guides provide consistent widths.
Trimming and Flattening
Routers are often used to trim and flatten the edges and faces of wood boards and panels. An edge trimming bit can shave off uneven edges or precisely trim boards and laminates to consistent widths.
A bottom cleaning bit helps level and smooth out surfaces by removing high spots and cutter marks. Flattening uneven stock saves time compared to hand sanding. This helps achieve perfectly flat surfaces for laminating, joinery, and finishing.
Creating Inlays and Decorative Patterns
Decorative inlays, textures, and patterns can be created on wood by removing material in precise shapes using a router. With guide bushings and patterns, any design can be routed onto wood surfaces. Geometric, abstract, and organic patterns are possible.
Intricate inlay designs made independently can be inset into routed cavities. Complex marquetry in exotic wood veneers can also be achieved this way. This allows near-endless creative possibilities for elevated decorative elements in woodworking.
Routing Signs and Lettering
Precise and professional-looking routing of lettering, serial numbers, and logos onto wood surfaces is easily achievable with the right router guide bushings, templates, and bits. Signs and serial numbers on products look clean versus hand-carving.
Small characters can be accurately reproduced once the router templates are made – allowing batch production. Letter and number stencils help create individual characters by freehand routing. With care, small yet highly legible lettering can be achieved.
Router Safety Tips and Precautions
While routers are very useful, the high spinning speed of router bits and sharp cutters makes them potentially dangerous. Observing basic workshop safety is crucial.
- Always wear eye and ear protection when routing. Use masks to avoid inhaling fine dust.
- Make sure stock is secure. Avoid routing small or unstable stock that can twist.
- Don’t rush cuts or force the router. Make light passes. Forcing can cause the bit to jam and twist.
- Keep hands away from the bit. Grip well clear of the spinning cutter. Use stop blocks if needed.
- Adjust depth and expose the bit only as much as needed to avoid deeper accidental passes.
- Unplug when changing bits. Ensure bits are clamped securely before switching on.
- Maintain proper speeds. Don’t overload the motor.
- Make sure the power switch is off before connecting power or performing maintenance.
Observing basic precautions and using jigs, blocks, and clamping when required will allow you to route safely. Paying attention will help avoid injuries and achieve better results.
Safety Gear Checklist
| Safety Gear | Why It’s Needed | Recommended Brands |
|---|---|---|
| Eye Protection | Prevents eye injury | 3M, Honeywell |
| Ear Protection | Reduces noise | 3M, Honeywell |
| Dust Mask | Protects lungs from dust | 3M, Honeywell |
| Router Guard | Protects from accidental contact with the bit | Freud, Bosch |
| Work Gloves | Protects hands from cuts and splinters | Mechanix Wear, Carhartt |
| Router Stand | Provides a stable base for the router | Kreg, Rockler |
Conclusion
Wood routers are among the most versatile tools for both functional woodworking like for Beginners, as well as decorative and artistic elements. Their high rpm motors coupled with a vast range of shaped cutter bits allow near endless possibilities for shaping, texturing, joining, inlaying, carving, and designing in wood.
We looked at key router components, types, and most importantly – the best uses for a wood router in your projects. From decorative edging and complex joinery to hollowing, inlays and precision carving – a good quality router expands your woodworking capabilities. They allow bringing creativity and strength together in your work.
I hope this gives you ideas on how a wood router can be a very useful addition to your workshop and opens up new possibilities for your wood projects. Do explore all the techniques and add this indispensible tool to your skills. Remember to focus on safe practices. With that, a wood router will greatly expand the quality and creativity of your woodworking.